Welcome to the next segment of our series: From Depths to Skies: Exploring the Future Landscape of the U.S. Naval Power.
In this series, we aim to inform and engage our members and friends on behalf of Americans for a Stronger Navy. We examine the current and future challenges and opportunities for the U.S. Navy in maintaining its global leadership and superiority in the maritime domain.
In the previous segments, we covered various topics related to the U.S. naval power, such as The RAND perspective on the U.S. naval strategy and policy, including the recommendations and insights from their recent reports and publications. An interview with Captain Brent Sadler, a former naval officer and a current professor at the Naval War College, on his views and experiences on the U.S. naval strategy and policy.
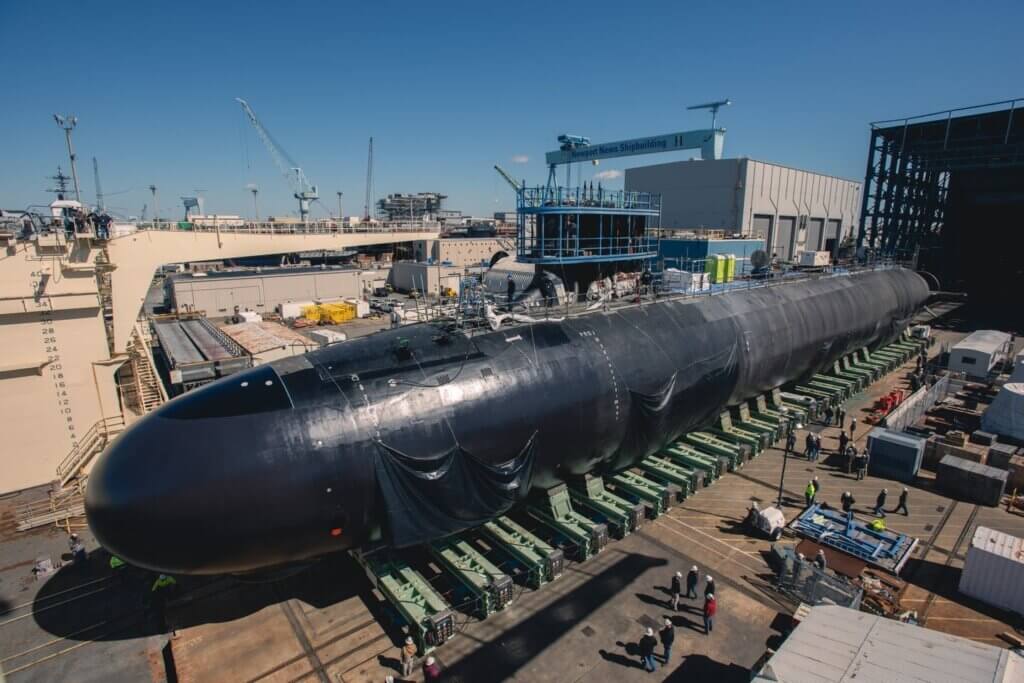
US Navy Submarine Fleet Deep Dive
In this segment, we will focus on one of the most important and complex elements of the U.S. naval power: the submarine fleet. We will dive deep into the issues and options for the future of the submarine fleet and into the myriad aspects of U.S. naval strength and its potential trajectory. Your insights, concerns, and support drive the transformation of the Navy, securing our nation’s future.
The submarine fleet is one of the most important and complex elements of the U.S. naval power. It provides stealth, deterrence, and strike capabilities in various domains and regions.
However, the fleet also faces many challenges, such as aging platforms, maintenance backlogs, rising costs, and growing threats from adversaries.
In this series:
- We’ll dive deep into the issues and options for the future of the submarine fleet.
- Examine the current status, plans, and priorities of the Navy for its submarine force structure, acquisition, and modernization.
- Review the perspectives and concerns of various stakeholders, such as lawmakers, analysts, critics, and allies.
- Finally, we will explore some of the reports and studies that have been published on this topic and provide our own analysis and recommendations
Columbia-class Program
The Navy is charting its course to design and build 12 new ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs), set to succeed the Ohio-class SSBNs.
This is no minor endeavor—it’s the Navy’s pinnacle priority, representing a foundational element of our strategic deterrence.
Issue: A significant challenge emerges in the form of schedule risks. A delay in the delivery of the lead ship could compromise the Navy’s objective of ensuring at least 10 SSBNs are consistently available for deterrence patrols.
The Navy’s FY2020 30-year shipbuilding plan outlines that, given a timely procurement and an 84-month construction timeframe, a stable fleet of 10 SSBNs will be operational from 2030 for about nine years.
Pro: The new Columbia-class will reinforce our nuclear deterrence, with enhanced stealth, improved endurance, and cutting-edge communication capabilities over the Ohio-class.
Con: Financially, the program could demand a lion’s share of the Navy’s shipbuilding budget, overshadowing other initiatives or requiring additional funds from Congress.
Cost of Replacing the Navy Fleet
The fiscal implications of rejuvenating the Navy’s 296-ship fleet over the upcoming three decades are significant. Current projections place the cost around $31 billion annually, marking a 50% increment from the past three decades.
Issue: With intentions to acquire both Virginia-class and Columbia-class submarines concurrently, costs are set to soar. The anticipated annual spend for the next decade is estimated at $11 billion, more than double the previous decade.
Pro: Such an investment would culminate in a technologically superior and larger fleet by 2051. However, the operational and maintenance bills will also swell.
Con: This financial commitment could surpass previous shipbuilding budgets, prompting potential reallocations within the defense sector or elsewhere in the government.
Weapon Systems Annual Assessment
An analysis of 121 major defense acquisition programs (MDAPs) reveals shifts in cost, timelines, and technological maturity. From FY2019 to FY2020, the MDAPs’ acquisition cost surged by $8 billion, totaling $1.8 trillion.
Issue: The Virginia-class submarine program, for instance, faced a $2.4 billion hike, attributed to increased labor, material costs, and engineering changes. Interestingly, future economic inflation rates might provide some offset.
Pro: This assessment offers a holistic, independent review of MDAPs, identifying both commendable practices and extant challenges.
Con: Persistent challenges spotlighted in the assessment might impede delivery and efficacy.
Autonomous Systems for ASW
As global submarine threats from nations like China and Russia escalate, the U.S. is exploring the potential of autonomous systems to fortify anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities.
The proposed paradigm emphasizes using UUVs, USVs, and UAVs in a distributed sensor network.
Issue: This ASW vision demands substantive investments to tackle technological, operational, and structural challenges. A dedicated Navy program office for autonomous ASW systems, equipped with authority and resources, is highly recommended.
Pro: The innovative approach could expand coverage zones, diminish risks, slash costs, and heighten manned platform survivability.
Con: Challenges span reliable communication, data security, integration with legacy systems, and compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Undersea Nuclear Arms Control
The viability of integrating submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and cruise missiles (SLCMs) in future nuclear arms control agreements demands attention.
Issue: Such integration might compromise the second-strike capability’s integrity. Addressing the U.S.-Russia asymmetry in nuclear triad reliance is imperative.
Pro: Integration could reduce accidental launch risks, foster strategic stability, and build trust among nuclear nations.
Con: Potential challenges encompass verification, negotiation complexities, and diverging interests among stakeholders.
Why It Matters: The Bedrock of National Security
The power of a nation is often measured by the might of its military, and at the heart of the United States’ defense strategy lies its naval force. The U.S. Navy, with its vast expanse of ships, submarines, and personnel, stands as a beacon of strength, ensuring the security of American shores and safeguarding its interests abroad.
But why should the average American care?
Every time we turn on the news and see international conflicts, trade negotiations, or discussions about global power dynamics, we are witnessing the ripple effects of naval strength and strategy.
A powerful navy ensures that the U.S. has a say in global matters, preserving peace, ensuring open sea lanes for trade, and offering a deterrence against potential adversaries. For the common citizen, this means a stable economy, job opportunities, and the assurance that they can sleep peacefully at night knowing they’re protected.
Moreover, as the geopolitical landscape shifts, the U.S. Navy’s strategy and fleet composition will inevitably change to counter emerging threats.
The decisions made today will shape the security and prosperity of future generations. It is, therefore, paramount for every American to be informed, engaged, and supportive of the endeavors that fortify the backbone of our nation’s defense: the U.S. Navy.
We profoundly value your continued engagement with Americans for a Stronger Navy. Together, we chart the course for a resilient, advanced, and secure naval future.
We invite you to follow along and read these reports as we delve into this important and timely topic. We also welcome your feedback and suggestions as we seek to inform and engage our members and friends on behalf of Americans for a Stronger Navy.
The time to act is now. Stay tuned for more updates soon. Until next time, fair winds and following seas!