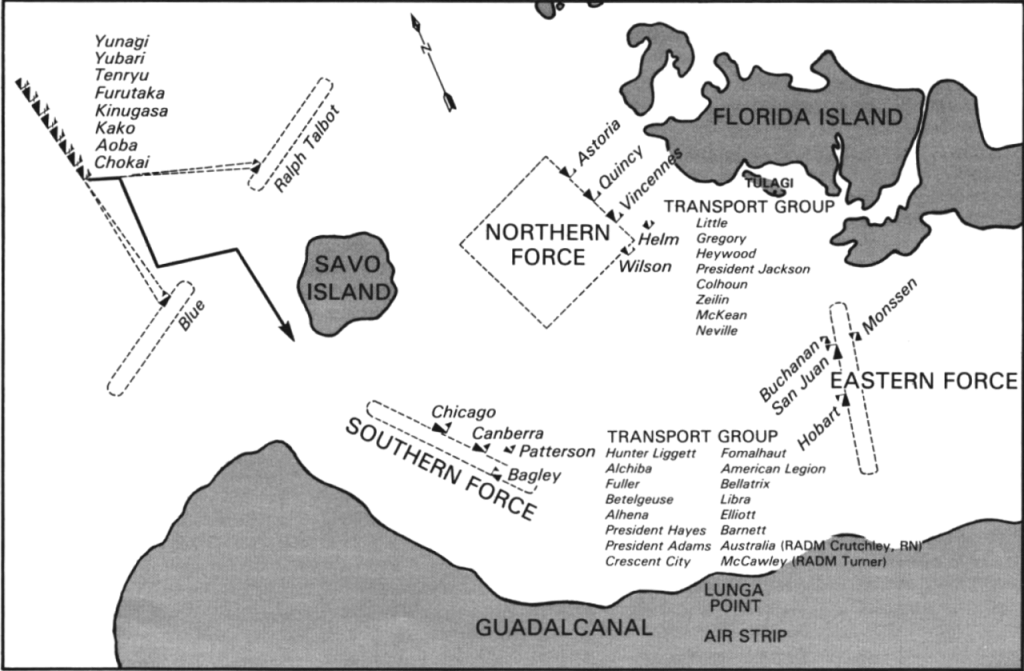

Introduction
On this solemn anniversary of the Battle of Savo Island, Americans for a Stronger Navy joins our Australian allies in remembering the courage and sacrifice of those who gave their lives in the dark waters off Guadalcanal on August 9, 1942.
The loss of HMAS Canberra and her 84 brave sailors, alongside over 900 American naval personnel, represents more than numbers—it represents the ultimate sacrifice made by free nations standing together against tyranny. This battle, while tactically a defeat, demonstrated the unbreakable bond between Australian and American naval forces that continues to secure the Pacific today.
The lessons of Savo Island—the critical importance of naval readiness, advanced training, and technological superiority—remain as relevant now as they were 82 years ago. As we face new challenges in the Pacific, from contested sea lanes to emerging threats, we honor these fallen heroes by ensuring our Navy maintains the strength, capability, and resolve they died defending.
Their sacrifice reminds us that freedom of navigation and maritime security are not abstract concepts, but principles worth defending with our lives. Today, as then, a strong Navy remains America’s first line of defense and our greatest tool for preserving peace through strength.
We stand with Australia in remembering these heroes and recommit ourselves to the naval strength that protects both our nations.
A Salute to Those Who Remember
To all who pause today to honor these fallen sailors—veterans, families, historians, students, and citizens both American and Australian—thank you. Your remembrance keeps their sacrifice alive and their lessons relevant. Whether you’re a descendant of a Savo Island survivor, a naval history enthusiast, or simply someone who understands that freedom isn’t free, your attention to this anniversary matters.
Special recognition goes to our Australian friends, military historians, naval societies, and educators who ensure these stories continue to be told. In an age of shortened attention spans, those who preserve and share naval history perform a vital service to both our nations.
Why Average Americans Should Care About the Battle of Savo Island
Economic Security The Pacific carries over $1.4 trillion in annual trade vital to American prosperity. These are the same trade routes where sailors died in 1942. Today, 40% of America’s imports cross these waters, along with critical shipping lanes for oil, gas, and renewable energy components that power our economy.
Historical Lessons for Today Savo Island showed the cost of being caught unprepared—a lesson directly applicable to current Pacific tensions. The battle demonstrated why strong allies like Australia are essential to American security, and how technological superiority matters. Japanese superiority in night-fighting capabilities led to their victory; today’s tech gaps could prove equally costly.
Personal Connection Many American families have ancestors who served in the Pacific Theater. Understanding what military service truly costs helps inform decisions about defense spending and foreign policy. The battle reminds us that the freedoms Americans enjoy came at tremendous cost and weren’t guaranteed by geography alone.
Current Relevance The same strategic waterways remain crucial to American interests today. Modern tensions in the South China Sea echo the naval competition of WWII, and historical battles like Savo Island inform current debates about naval funding and capabilities.
Strengthening Allied Partnerships
The Battle of Savo Island reminds us that America’s security depends not just on our own naval strength, but on the strength of our alliances. Today, this means:
The AUKUS Partnership with Australia and the UK builds on the naval cooperation forged in battles like Savo Island, sharing submarine technology that strengthens all three nations. Joint training exercises with Australian, Japanese, and other Pacific allies ensure we won’t repeat the communication failures of 1942 that contributed to the defeat.
Shared intelligence networks and integrated defense relationships born from WWII sacrifices now provide early warning and coordinated responses to regional threats. Allied shipbuilding and defense manufacturing strengthen both nations’ naval capabilities, creating an industrial base that supports deterrence.
The Battle of Savo Island isn’t just history—it’s a reminder that American prosperity and security depend on naval strength and strong alliances. The sailors who died there died protecting the world we live in today. Their legacy lives on not just in our memory, but in the enduring partnerships their sacrifice helped forge.
If we want peace, we must master this new domain.
It’s time to embrace it. It’s time to invest. It’s time to lead.
That’s why we launched Charting the Course: Voices That Matter—a 24-part educational series breaking down how we got here, what went wrong, and what must happen next. Our goal is simple: educate the public, connect the dots, and build the support needed to close the readiness gap before it’s too late.
Let’s roll.





