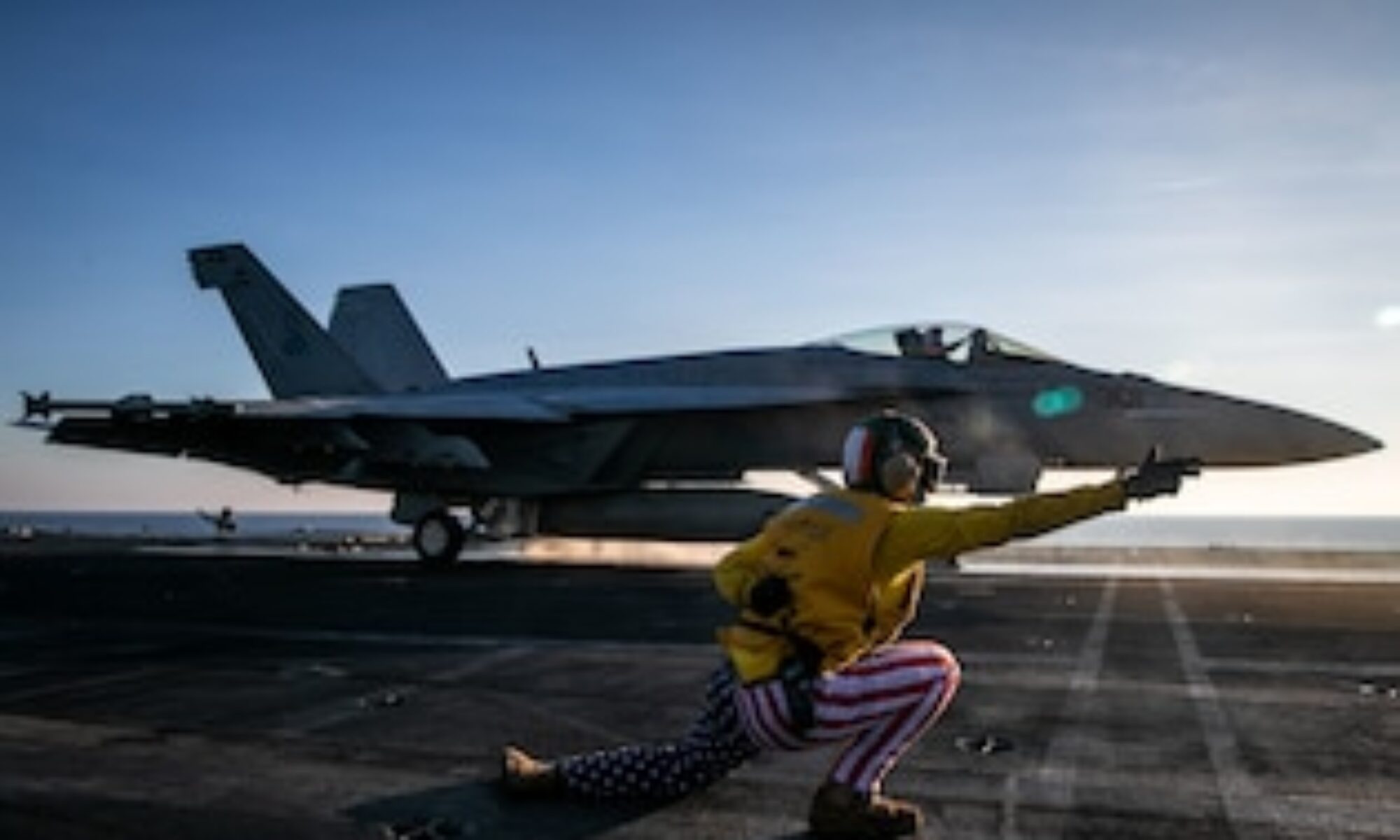
From the desk of Bill Cullifer, Founder of Americans for a Stronger Navy
Dear Mr. Zakheim,
I recently read your opinion piece in The Hill on October 18, 2024, titled “How the Navy Can Solve Its Submarine Shortage,” with great interest. Dov S. Zakheim, a senior adviser at the Center for Strategic and International Studies and vice chairman of the board for the Foreign Policy Research Institute, brings unparalleled expertise to this discussion. As a former undersecretary of Defense (comptroller) and chief financial officer for the Department of Defense from 2001 to 2004, as well as deputy undersecretary of Defense from 1985 to 1987, your insights on defense spending, strategic planning, and military capabilities are invaluable in understanding the complexities of the U.S. Navy’s submarine deficit.
The challenges the Navy faces in maintaining and expanding its submarine force are central to the security and operational effectiveness of the United States and its allies. At Americans for a Stronger Navy, we have long advocated for solutions to bolster our naval capabilities in light of growing global threats.
Your analysis of the potential for non-nuclear alternatives, including unmanned submarines and diesel-electric options, highlights viable paths for supplementing our fleet. However, after discussing these ideas with Captain Brent Sadler, U.S. Navy (Retired), Senior Fellow for Naval Warfare and Advanced Technology at The Heritage Foundation, a 26-year Navy veteran with extensive operational experience on nuclear-powered submarines and author of U.S. Naval Power in the 21st Century: A New Strategy for Facing the Chinese and Russian Threat, we are convinced that while these alternatives may fill certain gaps, they fall short of meeting the United States’ broader strategic needs. As Captain Sadler pointed out, “only nuclear-powered submarines possess the range, endurance, and strategic capabilities necessary to project power and safeguard the distant maritime choke points critical to both American and Australian interests.” This reality remains just as pertinent today as it was when Australia evaluated its own submarine needs decades ago.
The U.S. Navy’s dependence on nuclear-powered submarines stems not just from their superior endurance but from their ability to maintain forward presence in vital regions like the Indo-Pacific, where distances and operational demands far exceed the capabilities of diesel-electric subs. While unmanned systems like the Manta Ray and smaller ISR variants may enhance the fleet’s flexibility, they cannot replace the strategic depth provided by manned, nuclear-powered vessels.
Moreover, the capital infusion from Australia under the AUKUS agreement is a critical step toward increasing the production rates of Virginia-class submarines. Yet, as you astutely noted, even with this funding, workforce and industrial base shortages present formidable hurdles. The U.S. Navy must prioritize workforce development and shipyard modernization to accelerate production timelines and meet both our own force requirements and our commitments to allies like Australia.
At Americans for a Stronger Navy, we believe in advocating for a multifaceted approach—one that includes continued investments in nuclear-powered submarines, increased collaboration with our allies, and targeted support for the U.S. industrial base to reduce delays in production. This will allow us to respond effectively to the twin challenges posed by China and Russia, while also maintaining readiness in other volatile regions like the Middle East.
In conclusion, while unmanned and non-nuclear options can and should play a role in the future of undersea warfare, nuclear submarines remain the backbone of our strategy. We must remain steadfast in building and maintaining a fleet capable of meeting the global challenges of the 21st century.
Thank you again for your insightful analysis, and I look forward to further discussions on this critical topic.
Sincerely,
Bill Cullifer
Founder, Americans for a Stronger Navy
Note: I am not a paid spokesperson for any organization. My statements reflect my personal commitment to strengthening the U.S. Navy and advocating on behalf of those who serve.

