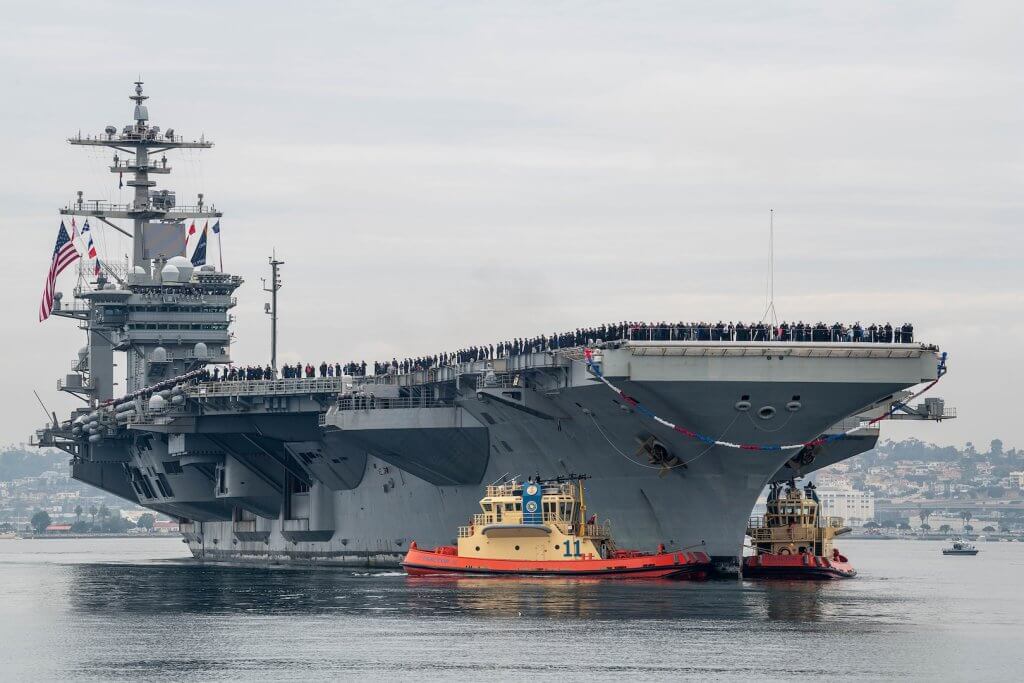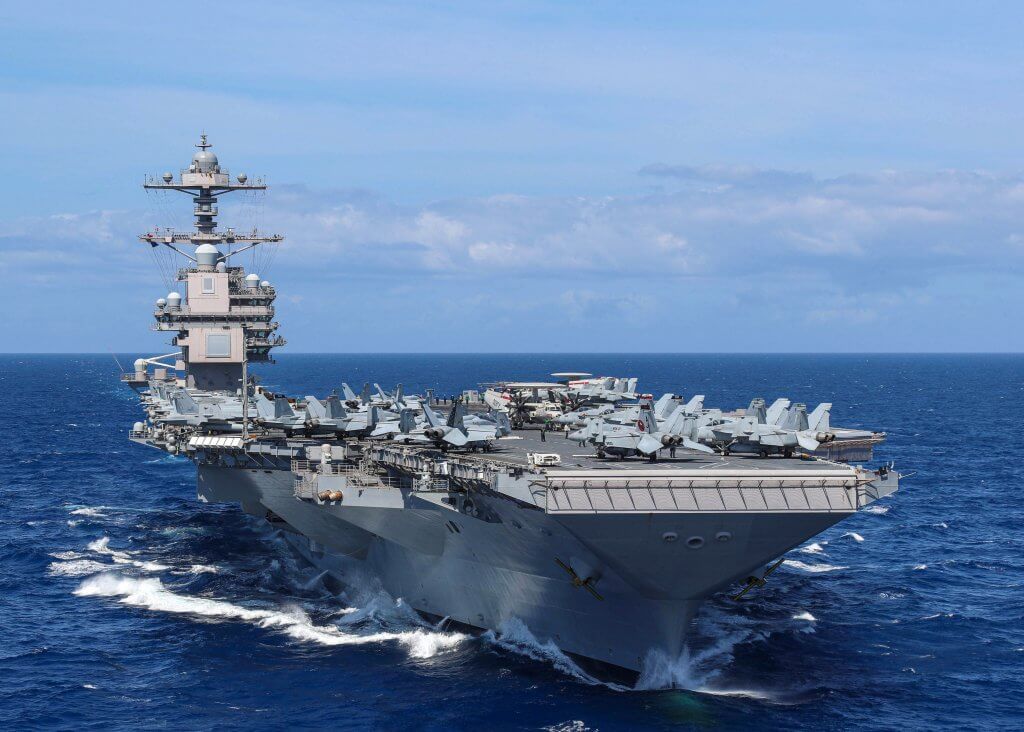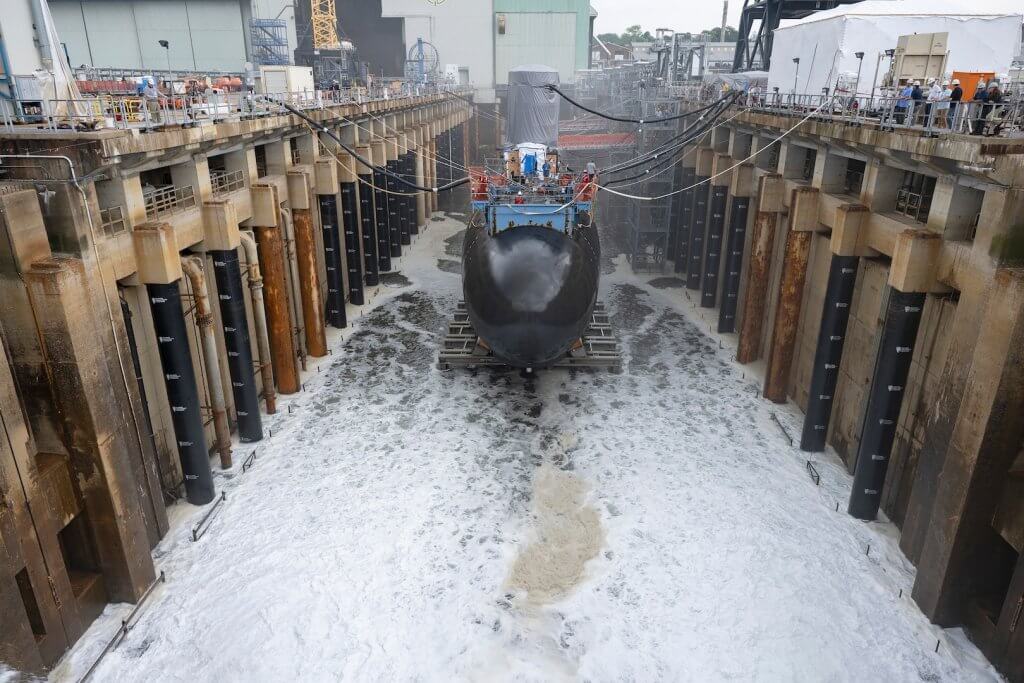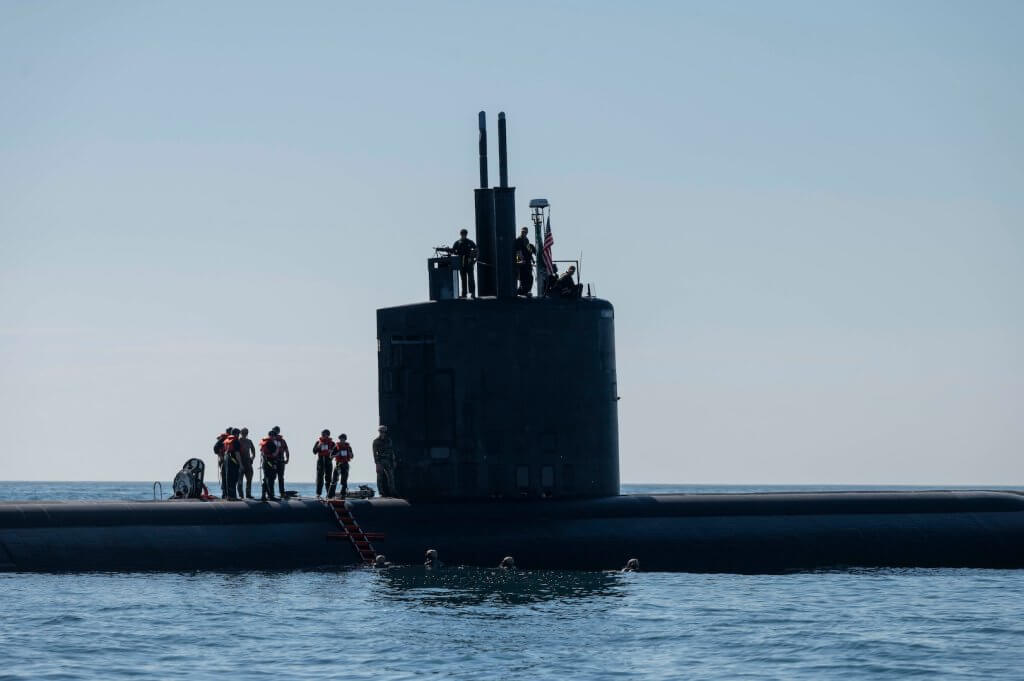

Welcome to this week’s edition of U.S. Naval News. At Americans for a Stronger Navy, we’re committed to keeping you informed about the latest developments from around the fleet. This week, we bring you key updates, including the USS Abraham Lincoln’s strategic deployment to the Gulf of Oman and cutting-edge advancements in drone operations aboard the USS George H.W. Bush.
But we’re not stopping there. In this edition, we’re introducing a new feature—an in-depth editorial commentary. Following the news, we’ll dive deeper into a critical issue affecting our Navy: the recent GAO report on the state of U.S. shipyards. This report raises alarms about the capacity and readiness of our shipyards to meet the demands of a modern Navy. We’ll explore why this matters, what needs to be done, and how you—our readers and supporters—can join us in advocating for change.
Your involvement is more important than ever. Together, we can make a difference.
Thank you for your continued support.
Operational Updates
- USS Abraham Lincoln Deployment: The USS Abraham Lincoln (CVN-72) has positioned itself in the Gulf of Oman as part of a broader strategy to maintain a strong naval presence in the Middle East. This deployment comes amid increasing regional tensions, particularly related to Iran’s activities.
- Theodore Roosevelt Strike Group Rescue: The USS Theodore Roosevelt Strike Group successfully rescued two distressed Iranian mariners in international waters. The rescue operation underscores the U.S. Navy’s readiness and commitment to maritime safety and humanitarian missions in the region.
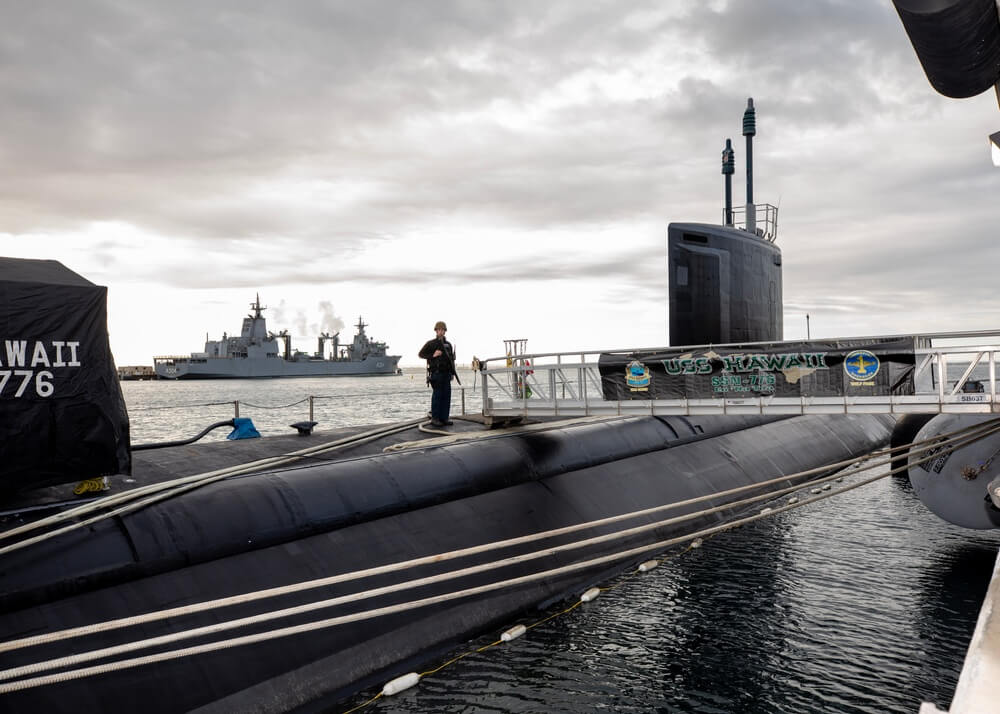
- Submarine Maintenance in Australia: The USS Hawaii (SSN 776) conducted scheduled maintenance at HMAS Stirling, Australia, under the AUKUS Pillar 1 initiative, which supports Australia’s development of a sovereign conventionally armed, nuclear-powered submarine capability.
- Bilateral Operations with Italian Navy: The U.S. Navy and Italian Navy conducted joint operations in the Philippine Sea, focusing on enhancing maritime security and demonstrating a unified commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific.
Technological and Strategic Developments
- Drone Command Center on USS George H.W. Bush: A new drone command center has been installed on the USS George H.W. Bush (CVN 77) to operate MQ-25 “Stingray” drones, marking a significant advancement in the Navy’s unmanned aerial capabilities.
- FY24 NDAA Shipbuilding Boost: The U.S. Senate’s version of the FY24 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) includes authorization for the procurement of 10 new battle force ships, emphasizing the ongoing modernization of the Navy’s fleet.
- China Watch: China recently claimed breakthroughs in autonomous vehicle technology, which could have significant military applications, including advanced driver-assistance systems and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). These developments are closely tied to China’s broader strategy of integrating military and civilian technology efforts.
- Russia Watch: Concerns continue to mount over the U.S. Navy’s readiness, particularly with regard to the availability of dry docks for essential ship repairs. U.S. lawmakers have voiced concerns about how this impacts naval operations, especially when compared to China’s rapid shipbuilding pace.
Community and Leadership News
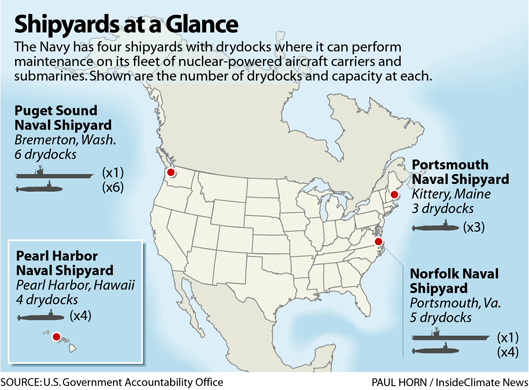
- Navy Shipyards Under Scrutiny: The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) has raised concerns about the capacity and efficiency of U.S. shipyards, emphasizing the need for modernization to keep pace with global naval demands. The GAO report, released on September 2, 2024, highlights that delays in ship repairs and upgrades could severely impact fleet readiness. The report also notes that inadequate infrastructure and workforce shortages are critical challenges that need immediate attention.
- Navy Wants Industry’s Help to Reduce Costs: Secretary of the Navy Carlos Del Toro has called on the defense industry to partner with the Navy in reducing sustainment costs, particularly by securing better terms for technical data rights in acquisition contracts.
Editorial: The Imperative to Modernize U.S. Navy Shipyards
The recent GAO report underscores what we at Americans for a Stronger Navy have been emphasizing for the past two years: the state of our Navy’s shipyards is a national crisis. The threats we face are real and cannot be overstated. As the GAO has highlighted, the current state of our shipyards directly threatens our fleet’s readiness and, by extension, our national security.
This is not just a Navy issue—it’s a national imperative. We cannot expect the Navy to shoulder this burden alone. It’s time for Congress to act decisively, providing the necessary funding and legislative support to modernize our shipyards. The Navy’s ability to maintain a robust, ready fleet depends on it.
We propose a multi-faceted approach to solving this crisis. A private-public-community partnership is essential to drive the changes needed. Industry leaders, local communities, and government must come together to build the workforce, improve infrastructure, and streamline processes to ensure our Navy remains the most powerful maritime force in the world.
We can no longer afford to point fingers. It’s time to move forward with a united effort. The future of our national security depends on it.
- Norfolk Naval Shipyard (NNSY)
- Location: Portsmouth, Virginia
- Established: 1767
- Specializes in: Overhaul, repair, and modernization of naval ships, particularly nuclear-powered vessels.
- Pearl Harbor Naval Shipyard
- Location: Pearl Harbor, Hawaii
- Established: 1908
- Specializes in: Overhaul, repair, and modernization of submarines and surface ships.
- Puget Sound Naval Shipyard (PSNS)
- Location: Bremerton, Washington
- Established: 1891
- Specializes in: Overhaul, repair, and decommissioning of naval vessels, particularly nuclear-powered ships and submarines.
- Portsmouth Naval Shipyard
- Location: Kittery, Maine
- Established: 1800
- Specializes in: Overhaul, repair, and modernization of nuclear-powered submarines.
- Huntington Ingalls Industries (Newport News Shipbuilding)
- Location: Newport News, Virginia
- Established: 1886
- Specializes in: Construction of nuclear-powered aircraft carriers and submarines, as well as ship repair.
- Mare Island Naval Shipyard (Closed)
- Location: Vallejo, California
- Established: 1854, closed in 1996
- Specializes in: Ship construction and repair (historically).
- Philadelphia Naval Shipyard (Closed)
- Location: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- Established: 1801, ceased operations in 1995
- Specializes in: Ship construction and repair (historically).
These shipyards represent a mixture of active and decommissioned facilities, but the active ones remain critical to maintaining and modernizing the U.S. Navy fleet, particularly in nuclear-powered ships and submarines.










