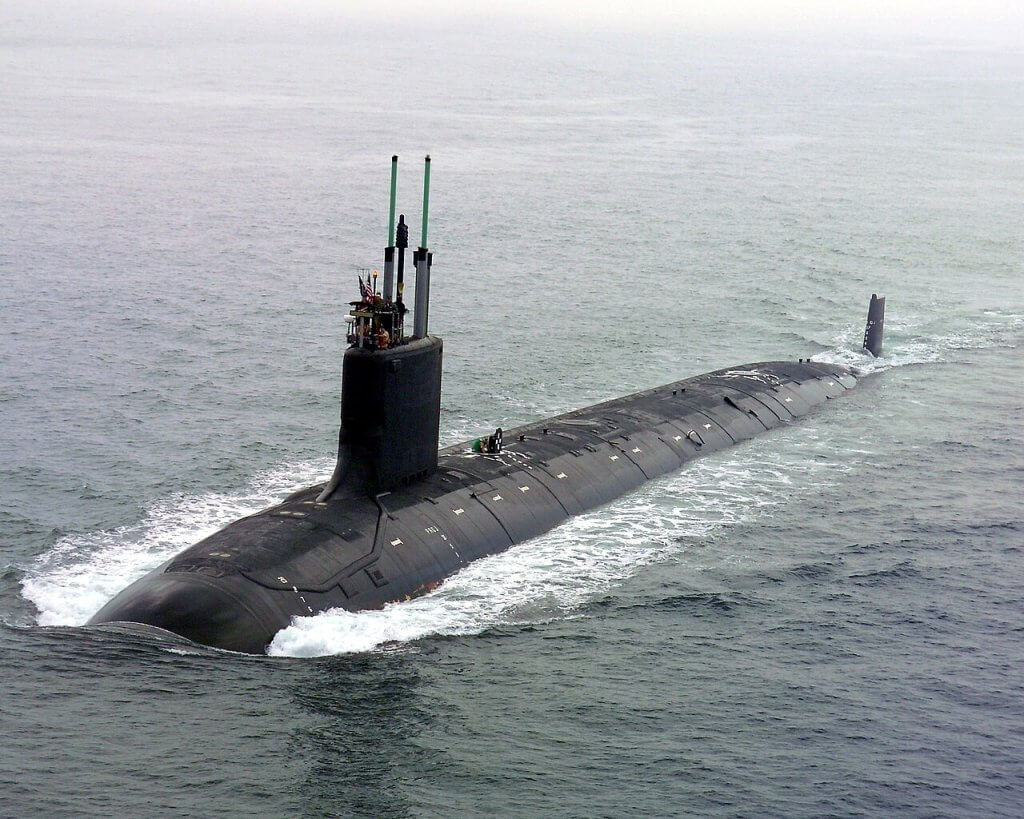
The recent $1.3 billion contract awarded by the Navy to General Dynamics Electric Boat for long-lead materials for the first Block VI Virginia-class nuclear attack submarines is not just another defense contract—it’s a strategic investment in America’s maritime dominance and national security. This contract, preceding an anticipated multi-year agreement, underscores the critical role these advanced submarines play in ensuring the Navy’s future capabilities.
Why This Matters to the American Public
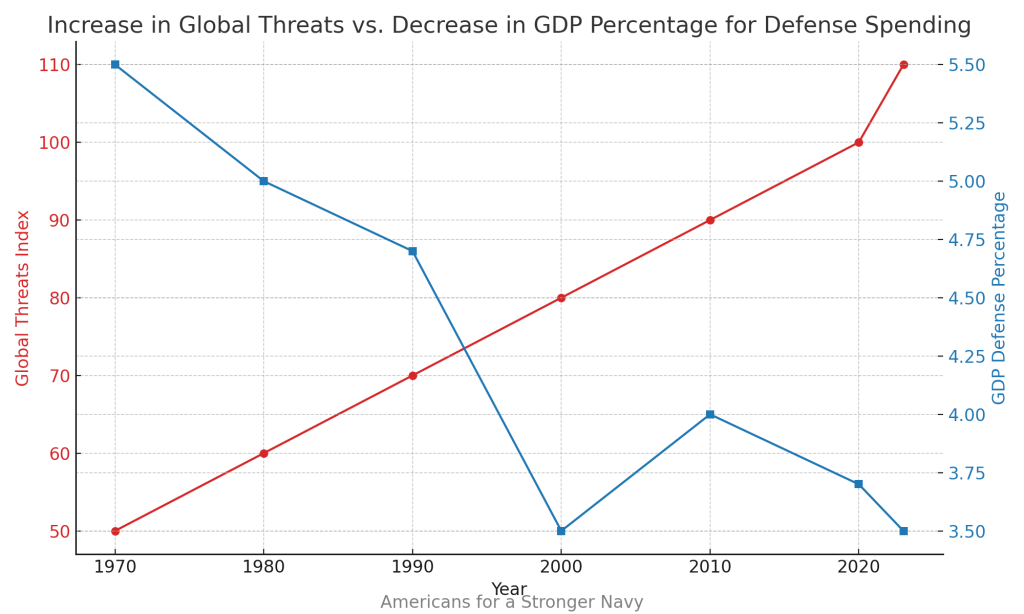
In a world where geopolitical tensions are rising, maintaining a robust and technologically advanced submarine fleet is crucial for protecting national interests and projecting power globally. The Virginia-class submarines, especially the Block VI with the Virginia Payload Module (VPM), are designed to meet these demands. These submarines will replace the aging Ohio-class guided-missile submarines, which have been a cornerstone of the Navy’s strike capabilities. The VPM-equipped submarines will ensure the U.S. Navy continues to have a formidable land strike capability, essential for deterring adversaries and maintaining strategic stability.
Understanding the Numbers and Their Implications
The $1.3 billion awarded for long-lead materials is part of a larger effort to secure the necessary components and materials for the construction of these advanced submarines. This contract sends a clear signal to suppliers and the defense industry to ramp up production capacity, ensuring the timely delivery of these vital assets. As Kevin Graney, President of General Dynamics Electric Boat, highlighted, consistent funding is essential to achieve the high-rate production the Navy requires.
Each Block VI submarine will feature the Virginia Payload Module, adding significant missile capacity with multiple all-up-round canisters (MAC). This enhancement is critical as the Navy prepares to decommission four Ohio-class guided-missile submarines, each capable of deploying 154 Tomahawk Land Attack Missiles. The new Block VI submarines will fill this gap, ensuring the Navy maintains its strategic land strike capabilities.
Implications for the Navy
The strategic implications of this contract are profound. The Block VI submarines represent the next generation of undersea warfare capabilities, providing the Navy with enhanced strike options and greater flexibility in mission planning. These submarines are not only designed for land strike missions but also for anti-submarine and surface ship warfare, special operations support, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
The investment in these submarines also supports the broader defense industrial base, ensuring that suppliers and manufacturers have the resources needed to meet the Navy’s requirements. This stability is crucial for maintaining a robust and responsive supply chain, capable of supporting high-rate production and innovation in submarine technology.
Looking Ahead: The Path to a Stronger Navy
The first Block VI boat is included in the Fiscal Year 2025 Pentagon budget request, currently being debated in Congress. This long-lead contract is a critical first step in securing the future of the Navy’s submarine fleet, ensuring that the United States maintains its strategic and tactical advantages. As the Navy and Electric Boat move towards finalizing a multi-year contract, the focus will remain on delivering these advanced submarines on time and within budget.
Rep. Joe Courtney (R-Conn.) praised the contract, noting that it provides procurement stability to supply chain vendors and keeps the industrial base moving forward. This stability is essential for promoting long-term investment in the capacity and materials needed for submarine production.
- Type: Nuclear attack submarine
- Displacement:
- Block I–IV: 7,900 t (8,700 short tons)
- Block V: 10,200 t (11,200 short tons)
- Length:
- Block I–IV: 377 ft (115 m)
- Block V: 460 ft (140 m)
- Beam: 34 ft (10 m)
- Propulsion:
- 1 × S9G nuclear reactor, 280,000 hp (210 MW)
- 2 × steam turbines, 40,000 shp (30 MW)
- 1 × single shaft pump-jet propulsor
- 1 × secondary propulsion motor
- Speed: 25 knots (46 km/h; 29 mph) or over
- Range: Unlimited
- Endurance: Limited only by food and maintenance requirements
- Test Depth: Over 800 ft (240 m)
Conclusion
The $1.3 billion contract for the Block VI Virginia-class submarines is more than just a financial transaction; it’s a strategic investment in America’s future security and naval supremacy. As we face evolving global threats, maintaining a cutting-edge submarine fleet is vital for deterrence and power projection. This contract represents a crucial step towards ensuring the Navy’s readiness and capability, reaffirming the United States’ commitment to maintaining a strong and technologically advanced maritime force.
In summary, the Virginia Block VI submarines are not just advanced pieces of military hardware—they are essential tools for preserving peace, responding to crises, and decisively winning conflicts if called upon. This investment in the Navy’s future is an investment in the security and prosperity of the American people.