A Cautionary Tale for U.S. Naval Planners and Taxpayers

Introduction
For decades, America chased profits by partnering with China — transferring technology and know-how that supercharged Beijing’s rise. Today, we could risk repeating that same mistake: putting quick Silicon Valley paydays ahead of America’s long-term security.
This is not about scoring points against Silicon Valley. It’s about ensuring America does not repeat the mistakes of the past — short-term profits and quick fixes that left China stronger and our Navy weaker — as someone who has seen these dynamics firsthand.
For those who have followed our work at Americans for a Stronger Navy, you know we believe America’s security, economy, and way of life depend on having the most capable fleet in the world. But capability isn’t measured in dollars spent or headlines about “innovation” — it’s measured in performance, reliability, and the safety of our sailors.
The latest reporting from Reuters makes clear we are falling catastrophically short, and that should alarm every American. Yes, bad news sells — but in this case, the bad news matters, because it reveals deeper failures in how America develops and fields naval technology — failures with life-and-death consequences.
When “Move Fast and Break Things” Breaks Lives
Recent tests off the California coast read like a Silicon Valley nightmare at sea. In one, a drone vessel stalled dead in the water while another smashed into its side, vaulting over the deck before crashing back into the sea. In another, a support boat capsized when the autonomous craft it was towing suddenly accelerated, throwing its captain into the ocean.
These aren’t beta test glitches. They’re life-threatening failures happening while China builds the largest navy in the world — and they’re funded by your tax dollars.
Testing vs. Accountability
Some will argue that testing is supposed to reveal problems — that dramatic failures are part of the process. They’re absolutely right that we need aggressive testing, not risk-aversion that slows innovation. But there’s a crucial difference between finding software bugs and throwing captains into the ocean. The same Silicon Valley companies that conduct exhaustive beta testing and gradual rollouts for consumer apps seem content to discover basic safety flaws during live Navy tests with human crews.
We’re not calling for less testing or slower innovation — we’re calling for the same rigorous pre-deployment standards these companies apply to their consumer products. If they can test a new iPhone feature through multiple phases before it reaches users, they can ensure autonomous boats won’t suddenly accelerate and capsize support vessels.
The Billion-Dollar Boondoggle
Defense startups with multi-billion-dollar valuations churn out drones by the dozen. Contractors take in hundreds of millions for autonomy software and systems that still stall, crash, and misfire. The culture of “fail fast” has migrated from app stores to the high seas — and our sailors are paying the price.
Bottom line: venture capitalists and defense contractors are getting rich while the Navy struggles to field systems that won’t sink, crash, or kill our crews.
History’s Warning — Don’t Hand China the Keys
We’ve been here before. In the late Cold War, the Navy realized that simply matching the Soviets ship-for-ship in Europe wasn’t enough. Leaders like John Lehman pushed a bold maritime strategy — using U.S. carrier groups to threaten the Soviet flanks, forcing Moscow to defend everywhere at once. That clarity of purpose built political support for a 600-ship Navy and helped secure the peace.
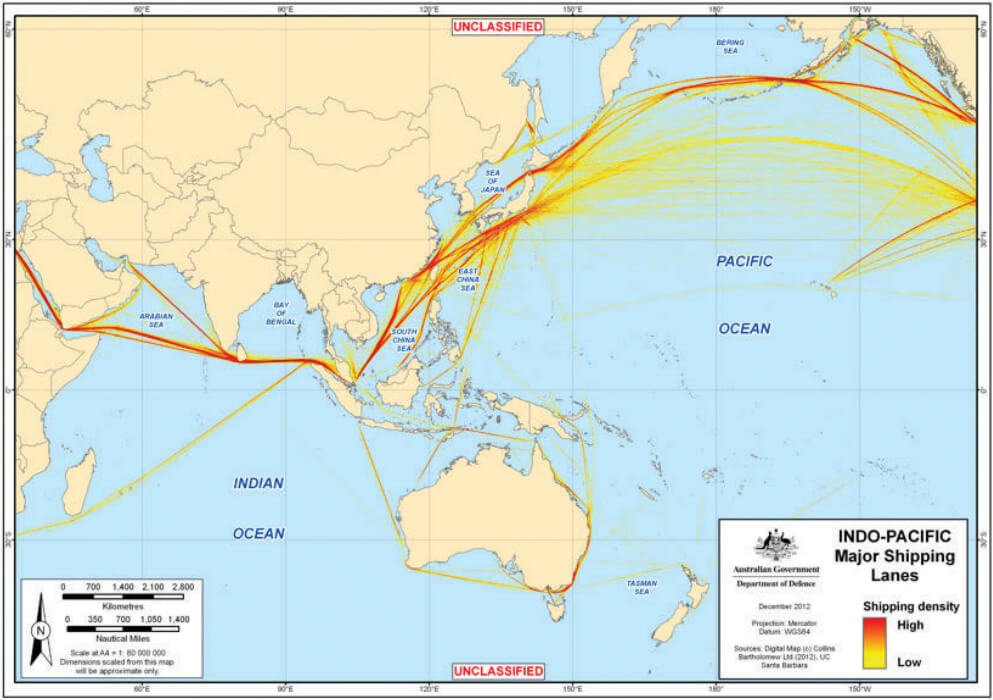
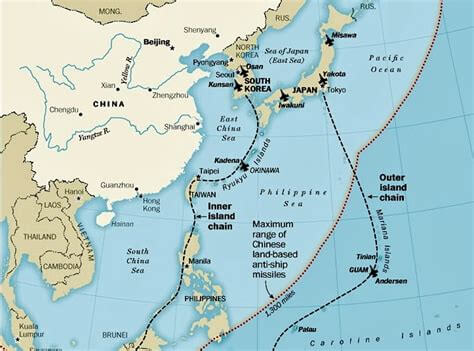
Today, by contrast, we risk drifting into the opposite: building expensive systems without a clear strategy, while China launches warships at breakneck pace. If Taiwan falls, Beijing won’t just seize an island — it will gain a springboard into the Central Pacific, threatening the Philippines, Guam, Hawaii, and the global sea lanes our prosperity depends on. That is the equivalent of handing China the keys to the Pacific.
The Tech Transfer Trap
For decades, Silicon Valley helped fuel China’s rise — chasing profits through partnerships, supply chains, and research deals that handed Beijing advanced technologies. That short-sightedness supercharged the very military now challenging America at sea. And today, the same ecosystem is cashing Pentagon checks while delivering half-finished products to the U.S. Navy.
Silicon Valley’s Responsibility
Palantir CEO Alex Karp recently said Silicon Valley must “fight for America.” We agree. But fighting for America means more than signing billion-dollar contracts — it means delivering technology that works, that protects sailors’ lives, and that strengthens deterrence in the Pacific. Anything less is not fighting for America; it’s profiting while our fleet falls behind.
We’ve seen how this plays out before: decades of short-sighted deals and technology transfers helped supercharge China’s rise. The result? Beijing got stronger, American taxpayers footed the bill, and now our Navy struggles with half-finished systems at sea. If Silicon Valley truly wants to defend America, it must also own its share of responsibility — and prove it by getting this right.
More Than Money — Lives and Liberty
This isn’t some procurement squabble over cost overruns. Every software glitch puts crews in mortal danger. Every failed deployment leaves the Pacific more vulnerable and our allies questioning American resolve. Every wasted dollar is one not spent on the ships, submarines, and systems actually needed to secure trade routes, defend allies, and deter Beijing.
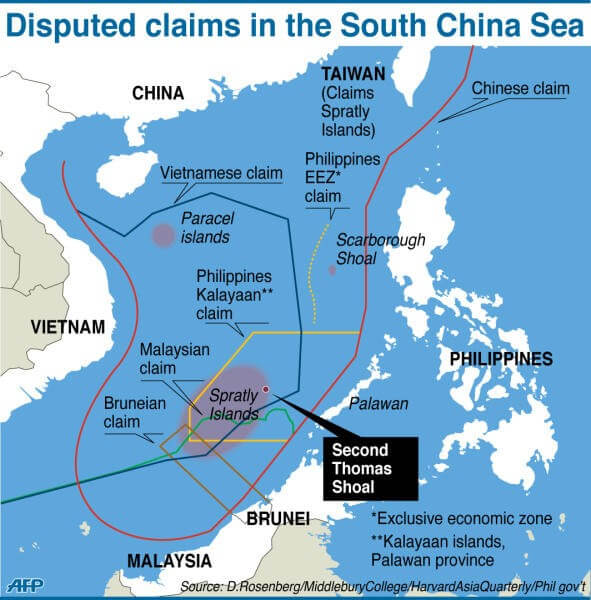
Just look at Scarborough Shoal, where Chinese vessels recently rammed and water-cannoned Philippine boats in defiance of international law. Or the swarms of “maritime militia” Beijing deploys daily to choke off its neighbors’ fishing grounds and shipping routes. These are not distant hypotheticals — they are live-fire tests of American resolve. While our drones crash into each other off California, China is rewriting the rules of the Pacific, one confrontation at a time.
While executives celebrate unicorn valuations in Silicon Valley, Chinese naval forces are conducting increasingly aggressive patrols in the South China Sea. While venture capitalists debate which startup deserves their next hundred million, China launches new warships at a pace that would have impressed World War II shipbuilders.
Demand Better — Or Lose Everything
America doesn’t need more press releases about “revolutionary defense innovation.” It needs results. Innovation is vital — America must harness Silicon Valley’s ingenuity — but innovation without accountability isn’t strength, it’s surrender. We are not calling for less innovation — we are calling for better innovation that delivers results worthy of the stakes.
We need accountability that goes beyond pausing contracts after people nearly die. We need a defense industrial base that prioritizes mission success over market valuations.
Don’t expect the mainstream press to frame this correctly — they’ll blame the Navy. But this isn’t on the sailors, the admirals, or the Navy’s acquisition officers working with the systems they’re given. This is on the defense contractors and tech companies who took taxpayer money promising cutting-edge capability and delivered dangerous prototypes instead.
America’s Naval Advantage — If We Seize It
Make no mistake: America still holds the cards to dominate the seas for decades to come. We have the world’s most innovative tech sector, the deepest capital markets, and the most experienced naval force on the planet. What we need is to stop letting Silicon Valley treat the U.S. Navy like a beta testing ground while they perfect their systems.
The same ecosystem that built the internet, revolutionized computing, and put rovers on Mars can absolutely build the world’s most capable autonomous naval fleet — if we demand they bring their A-game instead of their rough drafts. When SpaceX decided to take astronauts seriously, they revolutionized spaceflight. When Silicon Valley takes sailors seriously, they’ll revolutionize naval warfare.
This isn’t about stifling innovation — it’s about unleashing it properly. The companies cashing these Pentagon checks have proven they can build reliable, game-changing technology when their reputation depends on it. Now their reputation should depend on keeping our sailors safe and our Navy superior.
Most of all, we need Americans to demand better — because the alternative to demanding excellence isn’t just wasted money or embarrassing headlines. It’s watching China’s growing fleet face no credible opposition in the waters that secure our prosperity. But that’s not inevitable. America can still build the world’s most dominant navy — we just need to stop accepting second-rate work from first-rate companies.
The stakes are nothing less than our security, our economy, and our future. It’s time to make waves.
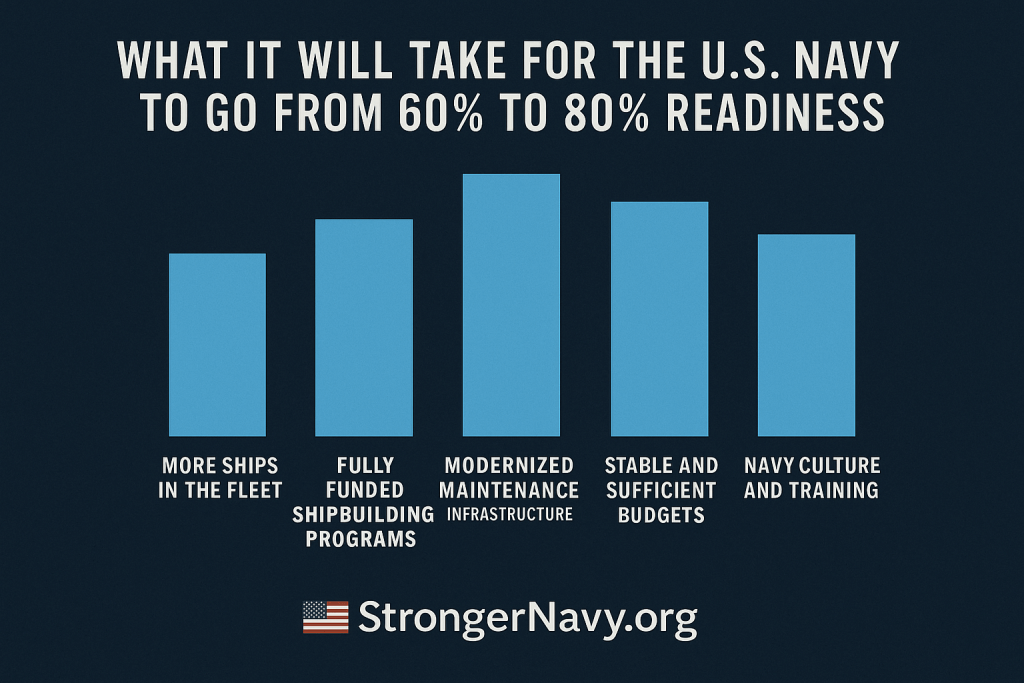
That’s why we launched Charting the Course: Voices That Matter—a 24-part educational series breaking down how we got here, what went wrong, and what must happen next. Our goal is simple: educate the public, connect the dots, and build the support needed to close the readiness gap before it’s too late.
Let’s roll.