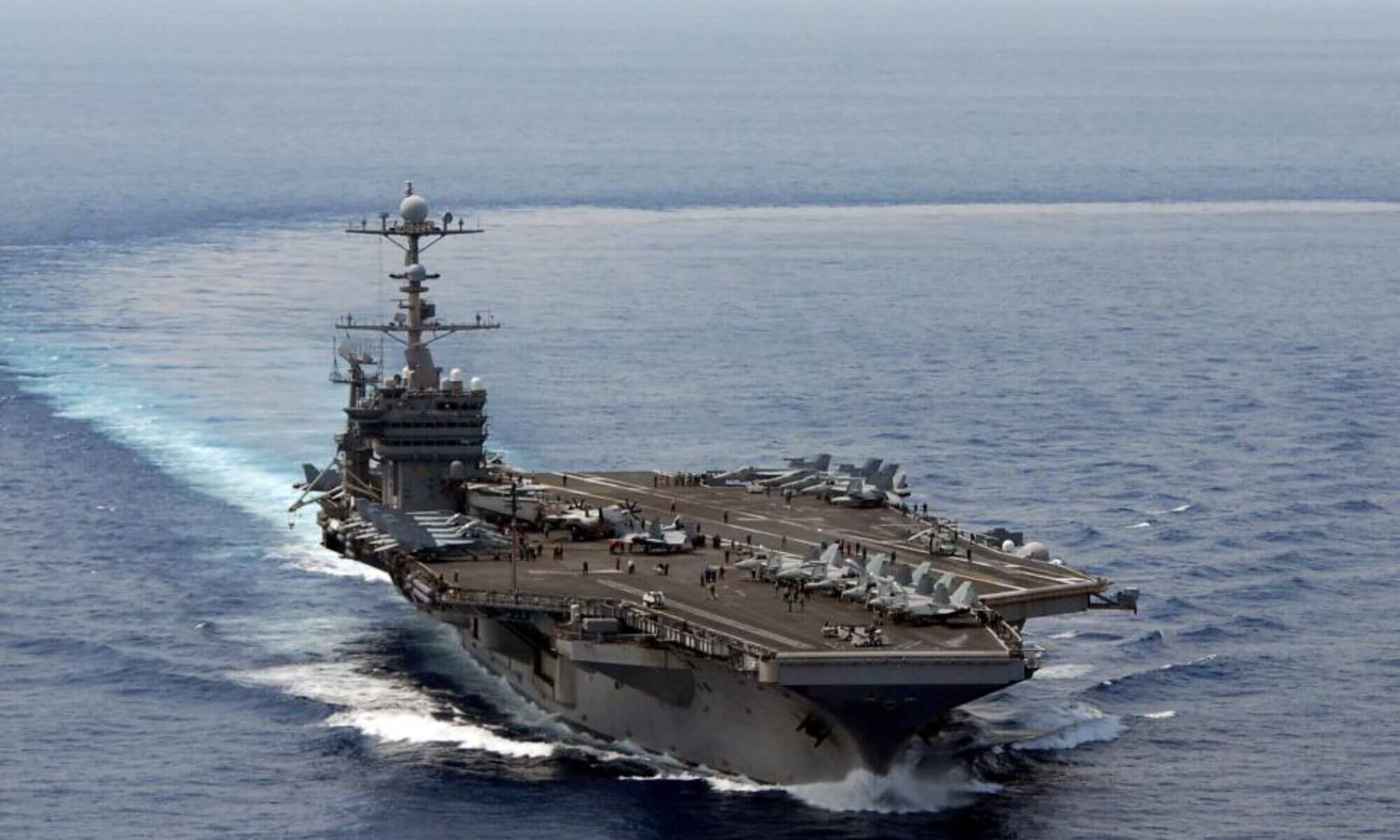
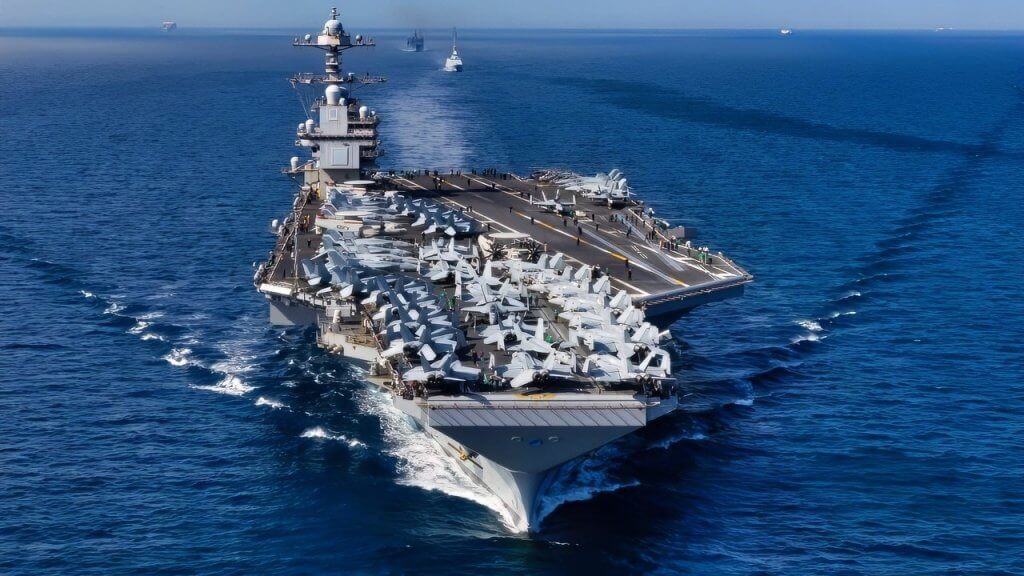
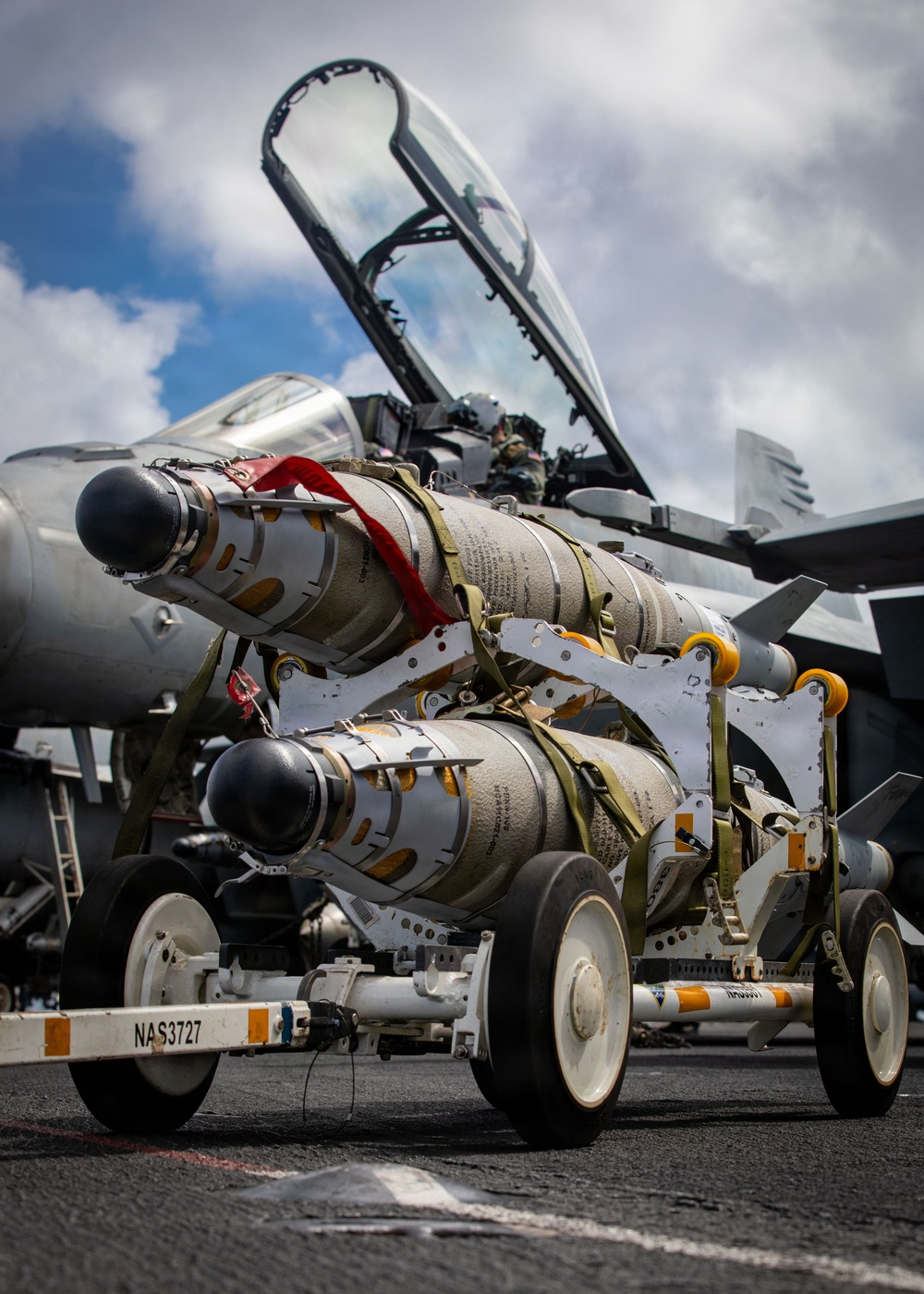
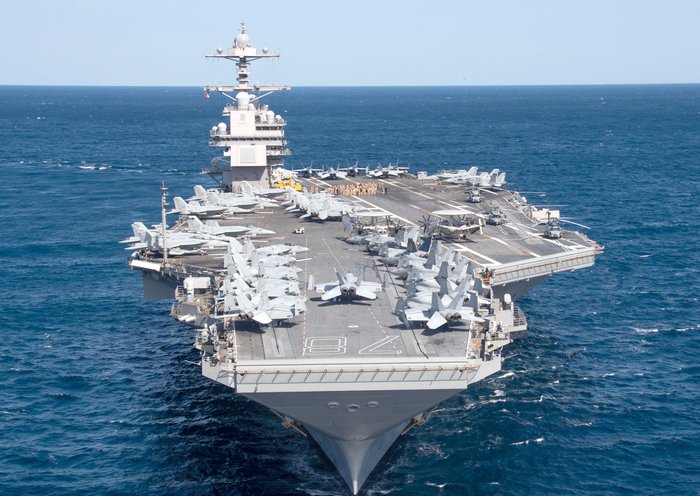
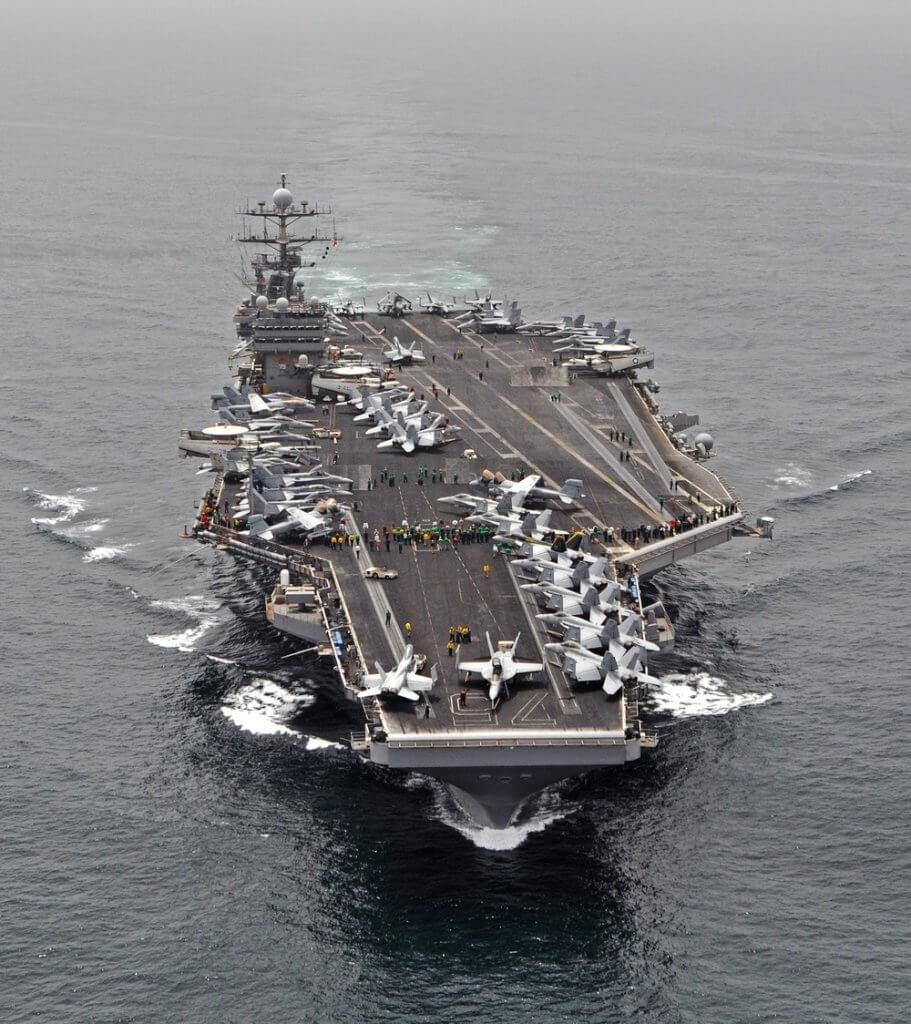
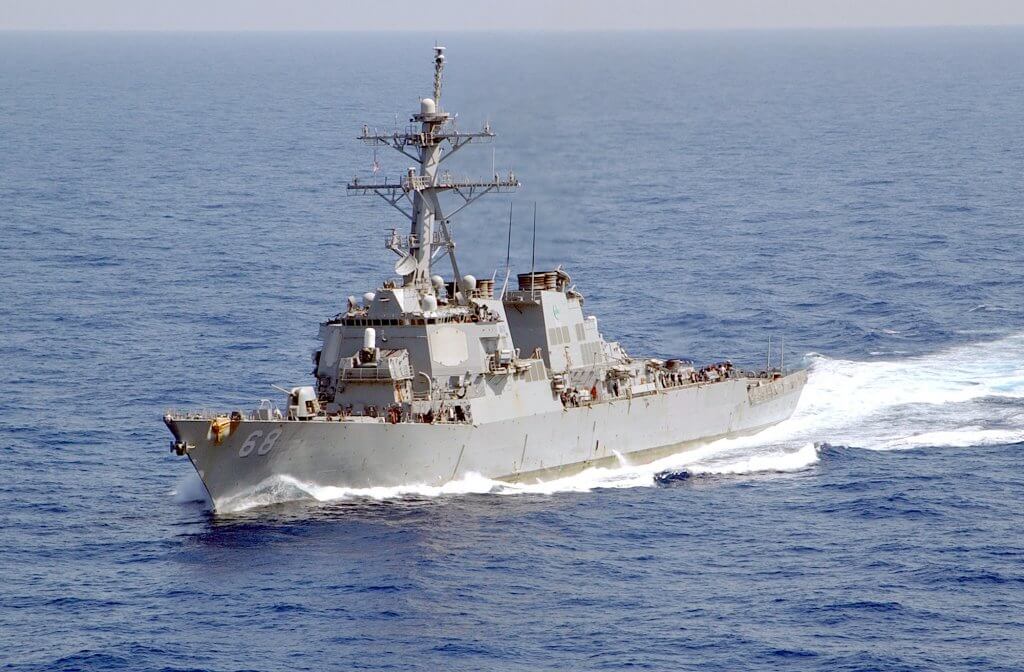
| USS Carl Vinson CSG | Aircraft Carrier Strike Group | North Arabian Sea | Security for US troops/bases in Gulf of Oman/Persian Gulf |
| USS Nimitz CSG | Aircraft Carrier Strike Group | Heading west from Indo-Pacific, arriving soon | Scheduled to relieve Carl Vinson, potential overlap |
| USS The Sullivans (DDG-68) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Eastern Mediterranean | Shooting down Iranian ballistic missiles for Israel |
| USS Thomas Hudner (DDG-116) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Eastern Mediterranean | Joined The Sullivans for defense strikes |
| USS Arleigh Burke (DDG-51) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Eastern Mediterranean (moved away) | Shooting down Iranian ballistic missiles for Israel |
| USS Forrest Sherman (DDG-98) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Red Sea | General presence, maritime security |
| USS Truxtun (DDG-103) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Red Sea | General presence, maritime security |
| USS Paul Ignatius (DDG-117) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Mediterranean Sea | Ballistic missile defense |
| USS Oscar Austin (DDG-79) | Guided-Missile Destroyer | Mediterranean Sea | Ballistic missile defense |
| Ohio-class guided-missile submarine (e.g., USS Georgia SSGN-729) | Guided-Missile Submarine | US Central Command AOR | Tomahawk missile launch platform |
| The USS Carl Vinson Carrier Strike Group (CSG) has been operating in the North Arabian Sea, strategically positioned to provide security for US troops and bases along the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf. Concurrently, the USS Nimitz CSG, long scheduled to relieve the Carl Vinson, is transiting from the Indo-Pacific and is expected to arrive in the region by the end of the month, potentially leading to a temporary overlap of the two carrier groups. This marks a rare occurrence, with two carriers operating simultaneously in the region for the second time this year. | | | |
| In terms of guided-missile destroyers, the USS The Sullivans (DDG-68) and USS Arleigh Burke (DDG-51) have been actively engaged in shooting down Iranian ballistic missiles targeting Israel in the Eastern Mediterranean. The USS Thomas Hudner (DDG-116) has since joined The Sullivans for continued defensive strikes, while the Arleigh Burke has repositioned. Additionally, the USS Forrest Sherman (DDG-98) and USS Truxtun (DDG-103) are positioned in the Red Sea , and five ballistic missile defense ships, including USS Arleigh Burke, USS Thomas Hudner, USS The Sullivans, USS Paul Ignatius (DDG-117), and USS Oscar Austin (DDG-79), are stationed in the Mediterranean Sea. Overall, the US has increased its troop presence in the Middle East to approximately 40,000, up from a typical 30,000, with bases on heightened alert. | | | |
| This significant re-prioritization of Middle East naval assets is evident in the deployment of a second aircraft carrier and the movement of naval vessels from potentially vulnerable locations like Bahrain. Bahrain, in particular, is home to the U.S. Navy’s Mideast-based 5th Fleet and has long been identified as a potential target for Iran. This shift occurs despite previous Pentagon efforts to focus on countering China in the Indo-Pacific. The increased naval presence signals a clear commitment to deterring Iranian aggression and protecting US interests in the Middle East, even if it entails potentially diluting focus on other strategic theaters. This could lead to a sustained, elevated naval presence, increasing operational tempo and potentially straining resources in the long term. | | | |
| The strategic implications of these naval deployments are profound. The increased presence restricts operational flexibility for Iran and necessitates a greater US naval presence in critical strategic waterways. The US 5th Fleet, headquartered in Bahrain, serves as a vital command center for naval operations across the Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea, and Red Sea, playing a crucial role in safeguarding the Strait of Hormuz and Bab el-Mandeb. This headquarters is now considered among the most likely Iranian targets. Bryan Clark has observed that US carriers have been operating less frequently within the confined waters of the Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz, instead spending more time in the broader Arabian Sea, a tactical adjustment in response to Iran’s increased capability to attack large surface ships. This adjustment highlights the enhanced maritime security challenges in these critical chokepoints, where the US Navy faces simultaneous and complex threats. The risk of multi-theater conflicts with significant economic consequences for global energy and trade is thus heightened, demanding continuous adaptation of naval strategy and force protection measures. | | | |
| Iranian Response and Retaliation Threats | | | |
| Iran has reacted with strong condemnation and explicit threats of retaliation following the US strikes, signaling potential repercussions for regional stability and global maritime security. | | | |
| Official Iranian Statements and Damage Assessment Claims | | | |
| Iran’s Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi vehemently condemned the strikes as a “grave violation of the UN Charter, international law and the NPT,” warning of “everlasting consequences” and asserting that Iran “reserves all options” to retaliate. Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian echoed this sentiment, condemning the US as the “primary instigator of the Zionist regime’s hostile actions”. While Iran’s Atomic Energy Organization confirmed the attacks on Fordo, Isfahan, and Natanz, it insisted that its nuclear work would not be halted. | | | |
| In a counter-narrative to US claims of “obliteration,” Iran’s National Nuclear Safety System Center and the IAEA reported “no signs of contamination” or “no increase in off-site radiation levels” at the targeted sites. An Al Jazeera official further claimed that the Fordo facility had been “long evacuated” and sustained no irreversible damage. This information warfare component underscores the regime’s efforts to manage both domestic and international perceptions of the strikes’ impact. | | | |
| Threats of Retaliation Against US Interests | | | |
| Tehran has overtly threatened retaliation against US interests in the region , with Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei warning of “irreparable damage”. Iran has explicitly named at least 19 US bases across the Gulf as potential targets, including the critical 5th Fleet Headquarters in Bahrain. | | | |
| A significant concern revolves around Iran’s potential disruption of critical global shipping lanes. Iran’s Parliament reportedly approved a measure to close the Strait of Hormuz, a vital chokepoint through which approximately 20% of global oil and gas demand flows. The final decision, however, rests with Iran’s Supreme National Security Council. Iran has previously threatened to deploy up to 6,000 naval mines and speedboats in the Strait of Hormuz, demonstrating a clear intent to disrupt maritime traffic. The multinational, US-led Combined Maritime Forces’ JMIC information center has categorized the threat to US-associated commercial shipping in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden as “high” following the strikes. | | | |
| Proxy Group Activities | | | |
| Iranian-backed proxy groups pose a significant threat to US interests. Houthi forces in Yemen have explicitly warned they would resume attacks on US ships in the Red Sea if Washington joined the bombing campaign against Iran. Their military has unequivocally stated its intent to attack US ships. Similarly, Kataib Hezbollah in Iraq has issued warnings of attacks on US interests and military bases in the region. Mohammed Albasha, an expert on Yemen, noted that “Now that the U.S. has struck Iran, I believe the Houthis, Kataib Hezbollah, and other Iranian-backed armed groups are most likely to attack U.S. interests”. He cautioned that “We have entered uncharted territory tonight, and nothing can be ruled out”. General Michael “Erik” Kurilla also highlighted that Iranian-backed militias had conducted approximately 200 attacks targeting US positions in Iraq and Syria between October 2023 and November 2024. | | | |
| Iran’s strategic dilemma becomes apparent in its response. While its rhetoric signals a strong intent to retaliate, assessments from figures like Gen. McKenzie suggest that Iran’s conventional ballistic missile and drone force “has been exposed as hollow” , and its primary proxy, Lebanese Hezbollah, has been “decapitated”. This indicates a degraded conventional capability, implying Iran will likely rely on asymmetric warfare and its proxy networks for retaliation, as emphasized by Albasha. This means the immediate threat to US naval assets and personnel in the region is less from a direct, conventional military confrontation and more from diffuse, non-state actor attacks, cyber operations, or maritime harassment in critical chokepoints. This necessitates a shift in US force protection and deterrence strategies to counter actors operating in the “gray zone” between peace and war, a concept explored by Michael Eisenstadt. | | | |
| The threats to close the Strait of Hormuz are not merely military but primarily economic. As 20-30% of global seaborne oil passes through this waterway, any disruption would trigger significant global economic shockwaves, impacting oil prices and shipping costs. Iran understands that its most potent leverage against the US and its allies may not be direct military confrontation but economic disruption. This places immense pressure on the US Navy’s 5th Fleet, whose primary mission includes safeguarding freedom of navigation in these waters. The potential for simultaneous maritime threats in both the Red Sea and the Strait of Hormuz further complicates US naval strategy and could necessitate difficult choices regarding resource allocation and escalation management. | | | |
| Finally, Iran’s immediate downplaying of damage and claims of “no contamination” , coupled with efforts to control information internally through internet blackouts and the detention of journalists’ family members , reflect a strong internal narrative control effort. This aligns with Seth G. Jones’ analysis of Iran’s “soft war” and information campaigns. This internal vulnerability could become a target for future “gray zone” operations, aiming to destabilize the regime through information warfare or by exacerbating internal frustrations. | | | |
| Expert Perspectives on the Conflict and Naval Implications | | | |
| Leading military and strategic experts offer diverse and often nuanced insights into the recent US strikes, Iran’s capabilities, and the broader implications for naval strategy and regional stability. | | | |
| Table 2: Notable Expert Commentary on US-Iran Naval Dynamics | | | |
| Expert Name | Affiliation | Key Statement/Insight | Source |
| — | — | — | — |
| Gen. Kenneth “Frank” McKenzie (Ret.) | Former CENTCOM Commander | Trump’s previous actions taught Iranians he “was not afraid to employ military power.” Threatening the nuclear program is key to threatening the regime. Iran’s missile/drone force “exposed as hollow.” Underground launch facilities are easier targets than deep nuclear sites. US basing strategy “outdated.” Iranians are “master negotiators.” | |
| Gen. Michael “Erik” Kurilla | CENTCOM Head | Provided “wide range of options” for strikes. Continuously assesses US posture and risk. Iran’s regional domination cannot be realized if regional states integrate with US. US is “transitioning from security guarantor to security integrator.” | |
| Adm. James G. Stavridis (Ret.) | Former Supreme US Commander in Europe | Trump’s two-week deadline might be a “very clever ruse to lull the Iranians into a sense of complacency.” | |
| Adm. Robert Natter (Ret.) | Retired US Navy Admiral | Iran has mines in Strait of Hormuz and missiles for US ships/sites; expects asymmetric response. | |
| Bryan Clark | Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments (CSBA) | “Only the US Has the Capabilities to Take Out Iran’s Nuclear Program.” Iran is “weaker and more vulnerable than it has been in decades.” US carriers operate less in Persian Gulf due to Iranian anti-ship capabilities. Iran could pull off “complex attack” causing damage/casualties. | |
| Seth G. Jones | Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) | Focuses on defense strategy, military operations, irregular warfare. Authored “Three Dangerous Men: Russia, China, Iran, and the Rise of Irregular Warfare.” US unprepared for irregular warfare, needs to leverage commercial sector. Iran engages in “soft war” and information campaigns. | |
| Michael Eisenstadt | The Washington Institute | Preventive attack likely “opening round of a lengthy campaign.” Iran would prioritize ballistic missiles for nuclear delivery. Believes Iran would use nuclear weapons only in extremis. | |
| Mohammed Albasha | Basha Report (Yemen expert) | Houthis, Kataib Hezbollah, and other Iranian-backed groups are “most likely to attack U.S. interests.” Expects “symbolic retaliation rather than full-scale escalation,” but “nothing can be ruled out.” | |
| Jonathan Schanzer | Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD) | “The nuclear program is no longer.” | |
| Andrea Stricker | FDD | Iran’s program “likely set back by years… which means more work ahead.” US/Israel need to ensure uranium stockpiles/centrifuges are recovered/destroyed. | |
| Captain Brent Sadler | Heritage Foundation | “Iran’s regime seems unable to change its tact, and is driving headlong into even more punishing attacks from USA. It is in fact a clear demonstration (if one needed) of the bloodthirsty worldview of the mullahs running Iran. The people of Iran have long been dissatisfied with the religious fanatics and its IRGC muscle, any crack in the regime’s brutality could rapidly see its demise – not regime change from outside but by Iranian people power.” | |
| Perspectives from Former CENTCOM Commanders | | | |
| General Kenneth “Frank” McKenzie (Ret.), who commanded US Central Command (CENTCOM) from 2019 to 2022, possesses deep familiarity with the Iranian threat. He posits that President Trump’s previous forceful actions have instilled in Iranians the understanding that he “was not afraid to employ military power”. McKenzie maintains that “threatening the nuclear program is a key element of any threat to the regime”. He assessed Iran’s ballistic missile and drone force as “exposed as hollow” following its unsuccessful attacks on Israel. McKenzie also suggested that “underground launch facilities are much easier to target than the deep nuclear sites”. He cautioned that the “window” for effective strikes “will not stay open forever,” as Iran will eventually replace air defenses and further harden its nuclear sites. Furthermore, McKenzie criticized the current US basing strategy in the Middle East as “outdated and poorly positioned to meet the central threat in the region: Iran,” advocating for a more flexible western basing network. He also noted that while “the Iranians aren’t particularly effective fighters, they are master negotiators”. | | | |
| General Michael “Erik” Kurilla, the current head of CENTCOM, is known for his hardline stance on Iran and his advocacy for aggressive military action. He confirmed having provided “a wide range of options” to the administration for strikes on Iran’s nuclear program. Kurilla emphasized the continuous assessment and adjustment of US posture and risk, stating that Iran’s goal of regional domination “cannot be realized if the region’s states continue to expand integration with each other and deepen partnership with the United States”. He also highlighted the US’s transition “from security guarantor to security integrator” in the Middle East. | | | |
| Commentary from Retired US Navy Admirals | | | |
| Retired Navy Admiral James G. Stavridis, former Supreme US Commander in Europe, speculated prior to the strikes that President Trump’s two-week deadline might have been a “very clever ruse to lull the Iranians into a sense of complacency”. Retired US Navy Admiral Robert Natter, commenting on the strikes, discussed Iran’s military capabilities, including its capacity to plant mines in the Strait of Hormuz and fire missiles at US ships and land sites, generally acknowledging Iran’s potential for asymmetric responses. | | | |
| Analysis from Leading Defense Think Tanks | | | |
| Bryan Clark, a senior fellow at the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments (CSBA), asserts that “Only the US Has the Capabilities to Take Out Iran’s Nuclear Program”. He believes Iran is “weaker and more vulnerable than it has been in decades”. Clark noted that US carriers have been operating less frequently in the Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz, spending more time in the Arabian Sea, as a direct response to Iran’s increased capability to attack large ships. He cautioned that Iran “might be able to pull off a complex attack that could degrade U.S. air defenses enough to get a couple of missiles through. It might not sink a ship, but it would certainly cause a lot damage and casualties and be a big public relations coup for the Iranians”. | | | |
| Seth G. Jones, President of the Defense and Security Department at the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), focuses on defense strategy, military operations, and irregular warfare. He authored “Three Dangerous Men: Russia, China, Iran, and the Rise of Irregular Warfare”. Jones highlights the US’s unpreparedness for the evolving nature of irregular warfare and the necessity of leveraging the commercial sector for capabilities such as battlefield awareness, unmanned systems, and influence operations against adversaries like Iran. He also points to Iran’s engagement in “soft war” tactics and information campaigns. | | | |
| Michael Eisenstadt, the Kahn Senior Fellow and director of The Washington Institute’s Military and Security Studies Program, specializes in Persian Gulf and Arab-Israeli security affairs and nuclear proliferation. In his work “Attacking Iran’s Nuclear Program: The Complex Calculus of Preventive Action,” he argues that a preventive attack will likely be “the opening round of a lengthy campaign” rather than a one-off event. Eisenstadt suggests that if Iran were to acquire nuclear weapons, it would prioritize ballistic missiles as its primary delivery system due to their survivability and penetration capabilities. He believes Iran would only use nuclear weapons in extremis, if the survival of the Islamic Republic were directly threatened. | | | |
| Captain Brent Sadler, a senior fellow at the Heritage Foundation, has weighed in on the strategic importance of targeting Iran’s nuclear facilities. He noted that Fordo, being “roughly 80 to 90 meters inside of a mountain,” is the “hardest target to hit” and requires American strikes with specialized weaponry like the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator, delivered by heavy bombers such as the B-2. Sadler also expressed hope for a peaceful resolution, suggesting that if the Iranian people “enact a regime change,” Fordo could be “taken peacefully and disbanded with the IAEA on the ground watching it happen in real time”. | | | |
| The collective expert commentary reveals an enduring debate regarding whether the recent strikes constitute a “decisive blow” or merely the beginning of a “protracted campaign.” While President Trump and some analysts like Jonathan Schanzer suggest the nuclear program is “obliterated” or “over” , more nuanced perspectives from Pentagon officials and think tank experts like Andrea Stricker and Michael Eisenstadt indicate a significant setback, not a definitive end. Eisenstadt’s framing of the attack as the “opening round of a lengthy campaign” underscores the strategic uncertainty surrounding the long-term impact. This implies that policymakers must prepare for a sustained effort to counter Iran’s nuclear ambitions, requiring ongoing intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) to detect rebuilding efforts , continuous diplomatic pressure, and the credible threat of further action. The “decisive blow” narrative, while politically appealing, may obscure the need for a more enduring and complex strategy. | | | |
| Furthermore, these expert analyses illuminate the evolving nature of deterrence in the Middle East. General McKenzie’s observations on Trump’s willingness to use military power and General Kurilla’s focus on “security integration” suggest a shift in US deterrence strategy. However, the persistent threats from Iranian proxies and Bryan Clark’s warnings about complex asymmetric attacks indicate that traditional military deterrence against a state actor may not fully address the “gray zone” tactics employed by Iran and its proxies. This necessitates that the US Navy and broader military adapt its deterrence posture to address both conventional and asymmetric threats. This involves not only maintaining superior firepower but also developing capabilities to counter drones, mines, and missile attacks from non-state actors, as well as enhancing regional partnerships for integrated defense. The vulnerability of US bases and naval assets to such attacks requires a re-evaluation of force protection and basing strategies. | | | |
| Finally, the interplay of military action and diplomatic leverage is a recurring theme. Vice President JD Vance’s statements about the strikes creating an environment for a “reset” of relations and an “opportunity for the Iranians to take the smart path” towards talks directly contrast with Iran’s Foreign Minister Araghchi’s assertion that the strikes have “blown up any possibility of diplomacy”. This highlights a fundamental disagreement on the role of military force in facilitating diplomacy. General McKenzie’s observation that Iranians are “master negotiators” who will “play for time” adds another layer of complexity. The military action, while intended to degrade Iran’s capabilities, simultaneously complicates diplomatic pathways. The US appears to be operating from a position of “peace through strength” , attempting to compel Iran back to the negotiating table from a weakened position. However, Iran’s strong condemnation and threats suggest a hardening of its stance, potentially making a diplomatic resolution more elusive in the short term. The long-term outcome will depend on whether military pressure can genuinely compel a shift in Iranian strategic calculus or merely entrench defiance. | | | |
| Broader Geopolitical and Economic Implications | | | |
| The US strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities have generated ripple effects that extend far beyond immediate military engagements, impacting global markets and the strategic balance across the Middle East. | | | |
| Impact on Global Oil Markets and Maritime Security | | | |
| The intensifying hostilities are poised to significantly affect global oil markets. Iran’s repeated threats to close the Strait of Hormuz, a critical global shipping corridor, would have profound consequences, leading to substantial increases in insurance premiums and costlier rerouting of oil shipments. Concurrently, the ongoing threat of Houthi attacks in the Red Sea could further disrupt shipping, elevate costs for global logistics companies, and diminish the strategic impact of Western naval forces in the region. The US thus faces simultaneous maritime threats in two strategically vital waterways: the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea. Beyond maritime trade, the conflict has already impacted air travel, with British Airways canceling flights to the UAE and Qatar and diverting a Dubai-bound airliner. Israel also responded by closing its airspace. | | | |
| This situation heralds a “new normal” of regional instability and supply chain vulnerability. The direct US intervention and Iranian threats to critical chokepoints indicate that the Middle East is entering a prolonged period of elevated instability. The rerouting of maritime traffic around the Cape of Good Hope and flight cancellations are immediate indicators of this new reality. Global energy and trade markets will likely experience sustained volatility and increased costs. Businesses and governments reliant on these routes will need to factor in higher insurance premiums, longer transit times, and potential disruptions, leading to a re-evaluation of global supply chain resilience and diversification strategies. This conflict, therefore, has far-reaching economic consequences that extend well beyond the immediate region. | | | |
| Evolving Strategic Balance and Deterrence Posture | | | |
| The direct involvement of the US signals a significant shift in Washington’s posture, increasing the likelihood of sustained Iranian retaliation against US personnel, assets, and allies in the region. In response, the US military has deployed additional fighter jets and refueling tankers to the region, and bases are on heightened alert. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth stated that the operation’s scope was “intentionally limited,” intended to send a specific message. General Kurilla emphasized that the US is “transitioning from security guarantor to security integrator” in the Middle East, necessitating a “sufficient and a sustainable posture” and improved foreign military sales to partners. Bryan Clark notes that Iran is “weaker and more vulnerable than it has been in decades,” with its proxies suffering major losses and expended missile inventories. The conflict presents significant geopolitical and economic risks, particularly in the energy, shipping, and security sectors, requiring ongoing monitoring and readiness for unforeseen circumstances. | | | |
| Outlook for De-escalation or Further Conflict | | | |
| The prospects for de-escalation remain precarious. UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres expressed grave alarm, warning of a “dangerous escalation” and a “growing risk that this conflict could rapidly get out of control — with catastrophic consequences”. While UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer emphasized de-escalation and negotiating a solution, simultaneously moving military equipment to protect UK interests , US Vice President JD Vance stated that America has “no interest in boots on the ground” and does not fear a “protracted conflict,” viewing the attacks as an “opportunity for the Iranians to take the smart path” towards talks. However, Iran’s Foreign Minister Araghchi countered that the US attacks “will have everlasting consequences” and have “blown up any possibility of diplomacy”. Regional security experts like Mohammed Albasha anticipate “symbolic retaliation rather than full-scale escalation,” but also caution that “nothing can be ruled out”. | | | |
| The challenge of de-escalation in this multi-actor conflict is substantial. Despite US assurances of “limited scope” and “no interest in protracted conflict” , and calls for de-escalation from international bodies, Iran’s strong rhetoric and its proxy network capabilities make rapid de-escalation difficult. The involvement of multiple state and non-state actors (Israel, US, UK, Iran, Houthis, Hezbollah) creates a complex web of interests and potential triggers. This conflict is highly susceptible to miscalculation and unintended escalation, where even “symbolic retaliation” could trigger further responses, leading to a tit-for-tat dynamic. The absence of direct communication channels between the US and Iran, coupled with differing interpretations of “deterrence” and “peace,” exacerbates this risk. International diplomacy remains crucial but faces significant hurdles in bridging the chasm created by direct military action. | | | |
| Furthermore, the situation presents a paradox of Iranian weakness and asymmetric strength. While experts like Bryan Clark and General McKenzie assert that Iran is “weaker and more vulnerable than it has been in decades” in terms of conventional military capabilities , its capacity for asymmetric warfare through proxies and disruption of maritime chokepoints remains a significant threat. This creates a scenario where conventional military superiority does not guarantee security. Consequently, the US and its allies cannot rely solely on conventional military might to achieve their objectives or ensure regional stability. A comprehensive strategy must address Iran’s asymmetric capabilities, its proxy networks, and its willingness to leverage economic chokepoints. This requires not only military readiness but also robust intelligence, cyber defense, and diplomatic efforts to counter malign influence and de-escalate proxy conflicts. | | | |
| Conclusion and Strategic Considerations | | | |
| The US strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities represent a critical juncture in Middle East security, marked by direct US military intervention and a heightened risk of regional escalation. The operation, “Midnight Hammer,” saw the US directly join Israel’s campaign against Iran’s nuclear program, employing advanced bunker-busting bombs and submarine-launched Tomahawk missiles against Fordo, Natanz, and Isfahan. The US Navy’s submarine force played a critical, covert role in these precision strikes, demonstrating deep-strike capabilities. This, coupled with significant surface fleet deployments, including two Carrier Strike Groups and multiple destroyers, underscores a substantial increase in US naval presence and strategic focus on the Middle East. | | | |
| In response, Iran has vowed retaliation against US interests and threatened to disrupt critical global shipping lanes, particularly the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea, through its own capabilities and proxy networks. Expert assessments regarding the long-term effectiveness of the strikes are mixed; while the facilities are severely damaged, analysts differ on whether this constitutes a definitive end to Iran’s nuclear ambitions or merely a significant setback that necessitates a protracted containment strategy. | | | |
| Based on this analysis, several strategic considerations emerge: | | | |