A Turning Point for America’s Maritime Strength
In a bold move aimed at restoring America’s maritime edge, President Donald Trump signed an executive order today (April 9, 2025) designed to revitalize the U.S. shipbuilding industry and reduce China’s growing control over the global shipping supply chain. The order calls for sweeping changes across trade, industry investment, and national security infrastructure—setting the stage for long-term renewal of America’s commercial and naval shipping capabilities.
What the Executive Order Includes
The new executive order establishes:
Maritime Security Trust Fund
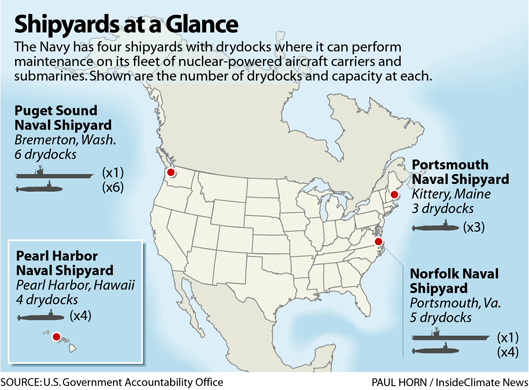
A dedicated fund to provide stable, long-term investment in shipbuilding, shipyards, dry docks, and repair facilities. Potential funding sources include tariffs, fines, port fees, and other federal revenue streams.
Port Fees on Chinese-Linked Ships
Ships flagged by China or built in Chinese shipyards may soon face significant docking fees at U.S. ports. The U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) is expected to finalize this remedy by mid-April. Allies will also be encouraged to implement similar restrictions.
Tariffs on Chinese-Made Cargo Equipment
The order directs the USTR to consider imposing tariffs on ship-to-shore cranes and cargo handling gear manufactured or assembled in China—or made with Chinese-controlled components anywhere in the world.
Enforcement of Harbor Maintenance Fees
To prevent workarounds, Homeland Security will crack down on companies trying to avoid U.S. fees by routing shipments through Mexico and Canada before transporting them across land borders.
Incentives for U.S. Shipyard Investment
The executive order includes provisions for incentivizing private sector investment in new or revitalized U.S. shipyards, commercial ship components, and critical maritime infrastructure.
Why Americans Should Care
The United States currently produces less than 1% of the world’s commercial ships—while China builds about 50%. In 1999, China’s share was just 5%. This trend has massive implications not just for economic competitiveness, but for national security and maritime logistics.
As President Trump put it:
“We used to build a ship a day, and now we don’t build a ship a year, practically. We have the capacity to do it.”
This executive order is more than policy—it’s a call to action.
Implications for the Navy
While the executive order does not explicitly mention the U.S. Navy, its impact on naval readiness and strategic capability is unmistakable. Revitalizing America’s commercial shipbuilding infrastructure strengthens the industrial base the Navy relies on for new construction, maintenance, and repairs. Investments in dry docks, skilled labor, and cargo handling capabilities bolster our ability to support fleet operations—especially in times of crisis.
Moreover, reducing reliance on Chinese-built shipping equipment and infrastructure directly supports U.S. naval strategy. It limits vulnerabilities in ports and logistics chains, while reinforcing America’s control over critical maritime assets. A stronger shipbuilding sector means a stronger Navy, even if it’s not named in the order.
Implications for Our Allies
The executive order sends a message to America’s allies: We are serious about maritime strength and expect partners to do the same. With Chinese-built vessels operating across global supply chains, coordinated action could limit strategic vulnerabilities and encourage diversified, allied-aligned shipping infrastructure.
A Statement from Americans for a Stronger Navy
“This executive order is a long-overdue step toward restoring our nation’s ability to build and maintain the ships we depend on for both commerce and defense. The Navy does not operate in a vacuum—it needs a healthy, resilient industrial base. America must lead again on the seas, not just militarily, but commercially. This is how we secure freedom of navigation, economic stability, and peace through strength.”
— Bill Cullifer, founder, Americans for a Stronger Navy
Your Voice Matters
This is our moment. Let’s celebrate the executive order—but keep pushing until America leads on the seas again. Congress must act, industry must respond, and Americans must stay engaged.
Sign up to be part of the movement. It’s free. A stronger Navy begins with a stronger nation.